Learning how to create a business case for SEO investment is an invaluable skill – whether you are working on an in-house marketing team or at a marketing agency.
The value and opportunity of including SEO (search engine optimization) in company marketing plans may be clear to you. But your company’s or clients’ stakeholders will benefit from a concise business case that summarizes the benefits, risks, cost and ROI of investing in SEO.
This article provides a business case for SEO framework you can use to clearly explain the following to current and potential clients:
- What SEO is
- What SEO isn’t
- Why to invest in SEO, including a list of benefits
- How Google ranks webpages
We also covered these elements in our webinar, The Business Case for SEO.
We’ve also included a template to help you create a “business case for SEO investment” for your clients and prospects that includes four parts:
- Summary: An overview of SEO and how it works
- Opportunity and Risk
- Cost Estimate
- ROI Estimate
Why Invest in SEO?
Research from Google published noted that 89% of B2B researchers use the internet during the B2B research process.
If you want your or your clients’ businesses to show up in search results for prospective customers, you need to make sure your website and content can be found. That means SEO shouldn’t be an afterthought. Rather, it should be integrated into your sales and marketing strategies. Following SEO best practices can drive real results for your business.
What is SEO and PPC?
SEO stands for search engine optimization. It is the process of optimizing a website to rank higher in search engine results pages (SERPs). And indeed, ranking higher up in the SERPs improves the online visibility of your business so you are best positioned to show up when people are looking for you and your product(s) and service(s).
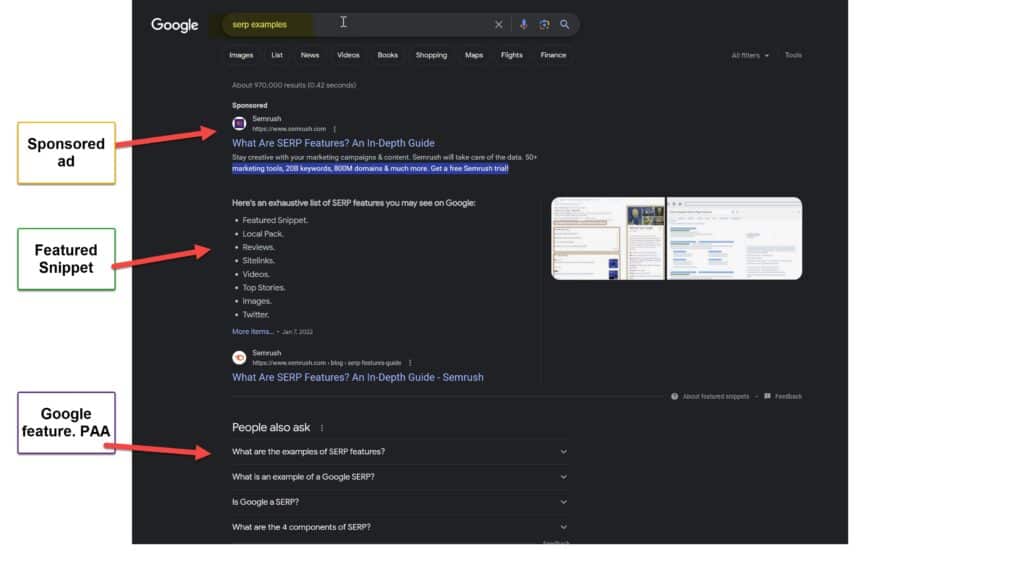
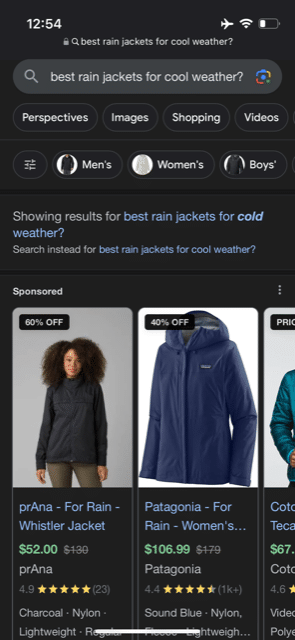
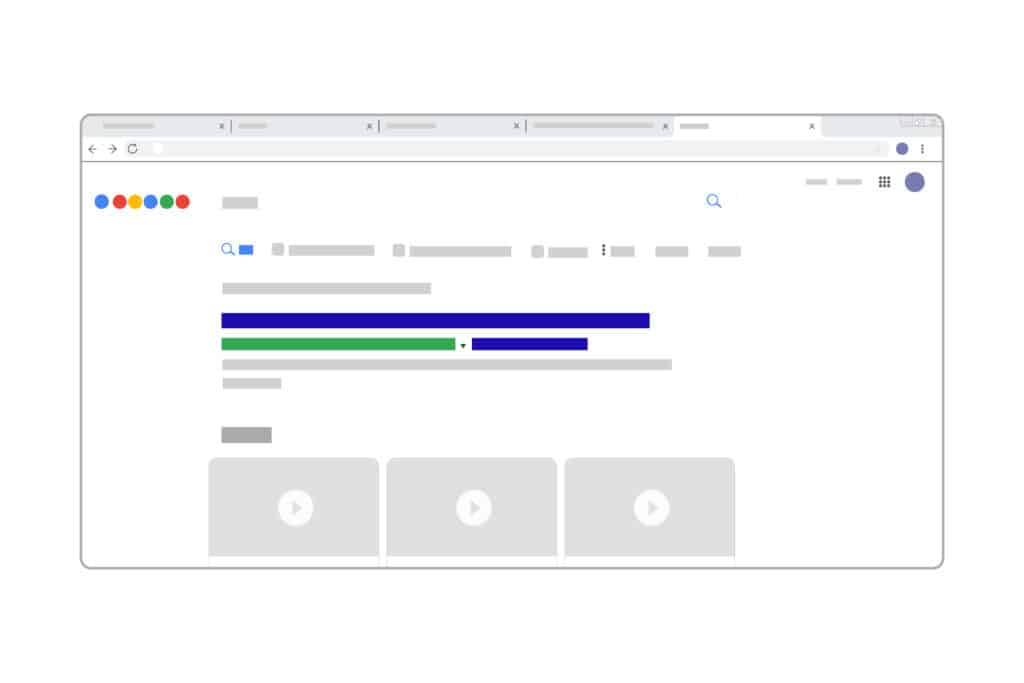
Google’s search engine results page is ever-changing. The first critical detail when reviewing a SERP is distinguishing between paid ads and organic search results.
PPC refers to pay per click advertising. Advertisers pay to run ads in the top positions on SERPs as part of their PPC strategy.
Organic, in this context, refers to results that no website can pay Google to appear in. Below you can see a simple graphic that illustrates the difference between paid and organic search results.

Examples of SERPs (search engine results pages)
Click Through Rate Google Search Results
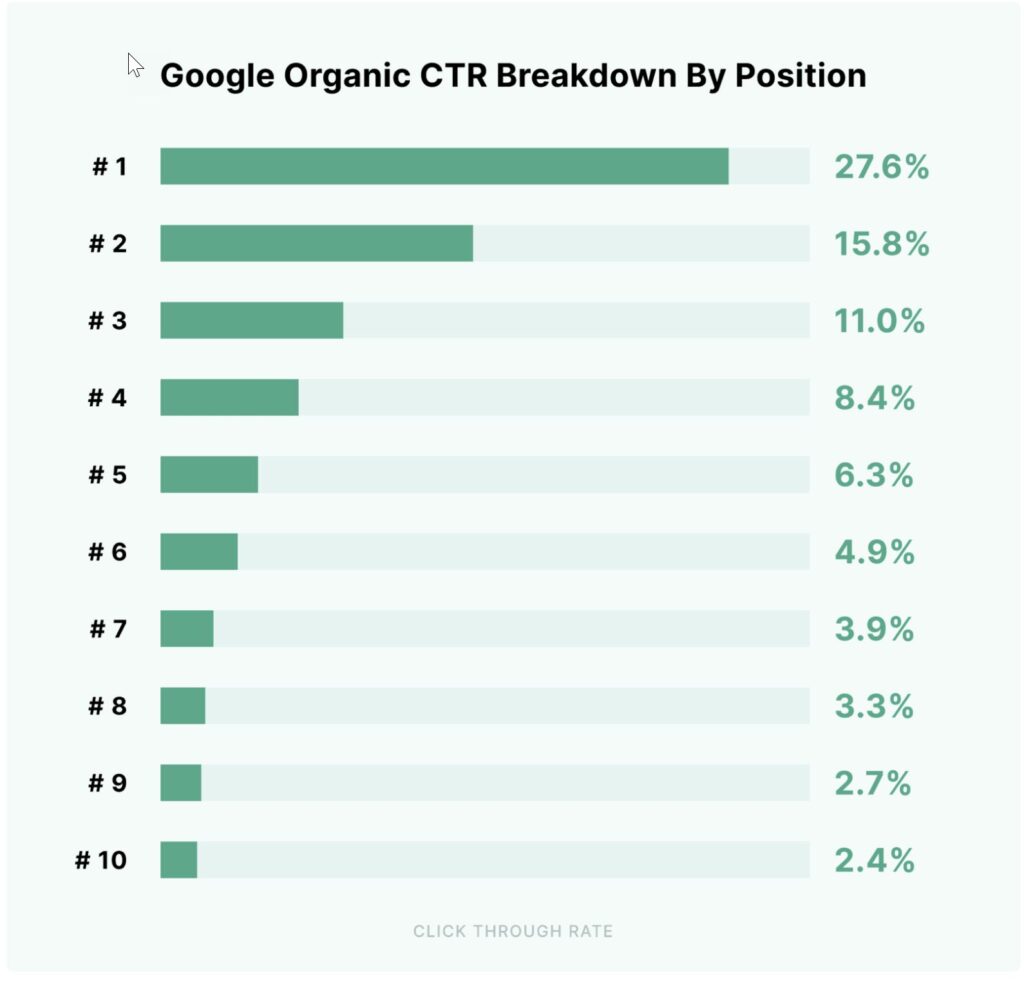
We can all probably guess that the search results that appear at the top of a SERP get clicked more frequently than results lower down the page. Backlinko, an SEO agency founded by Brian Dean and acquired in 2022 by Semrush, published a study of four million Google search results and found the following:
- #1 result in Google has a click-through rate (CTR) of 27.6%.
- #1-5 positions in Google have a sum CTR of 69.1%.
- #1-10 positions in Google have a sum CTR of 86.3%.
What Are the Basic Concepts of SEO?
Now that we’ve reviewed t how SERP position corresponds to click through rate, we arrive at the burning question: How do you get your webpage to appear in the top positions?
Webpages that rank well in organic search generally follow SEO best practices in the following key areas: technical, on-page and off-page.
Technical SEO:
Technical SEO is how you make sure nothing on your website’s backend is preventing it from being found and ranked highly by search engines.
See this great overview of technical SEO basics and best practices from Semrush. >>
On-Page SEO:
On-page SEO also involves optimizing web pages for search engines and users. This component focuses on optimizing page content and design so pages can rank higher in search results and attract more visitors. For instance, one on-page SEO practice involves including keywords you want to rank for are included in critical parts of your page, such as the page meta title, page meta descriptions, URL name, headers names and more.
Learn more in our resource for on-page SEO as it relates to blog posts. >>
Off-Page SEO:
Off-page SEO is the practice and process of building authority and trust for your website through external signals. The most crucial of external signals are backlinks from other websites, which are like votes of confidence.
Learn all about off-page SEO in HubSpot’s guide. >>
The tactics that fall under these SEO components help improve the visibility of the content you are creating.
What Are the Benefits of Investing in SEO?
SEO can help you:
Increase website traffic
When your website ranks higher in SERPs for the topics you want it to, more people will see it. This means more relevant traffic to your website, which can result in more leads and sales.
Build trust and credibility
When your website ranks high in SERPs, it shows potential customers that you are a credible and trustworthy source of information, products and/or services. Building that trust and credibility with potential customers can also result in more leads and sales.
Improve brand awareness
When your website is visible in SERPs, it helps improve brand awareness. People will see your website when searching for information about products or services that you offer – even if they don’t immediately click on your webpage links.
Improve user experience
A page that was created following SEO best practices will provide an optimal user experience. Why? If you start your content creation process by doing keyword research, you will home in on the intent for your visitors’ search queries. Therefore, you will ideally map the content to meet their intent. We all know how frustrating it is to click on a link thinking you’re going to find relevant information and then NOT find the information (products/services) you expected. SEO helps your target audience find products and services like yours.
Once a visitor has arrived at your page, following SEO best practices can improve the reading (and scanning) experience in the following ways:
- Providing a summary at top (an Executive Summary). This answers the primary question in the beginning.
- Making it an easy and enjoyable reading/scanning experience (bigger fonts, appropriate header sizes, chunked content, other related content that’s easy to click to)
- Providing a table of contents for longer pieces so the reader can quickly orient themselves and jump directly to the information they want.
Understand the voice of your customer
When you invest time and resources into SEO, using keyword research, searcher intent research and competitive analysis, you discover – from both your actual website search query data and other keyword search tools – what keywords bring users to your site and competitors’ sites. You unearth a goldmine of user language that can be infused into other marketing channels, such email and social.
How Does Google Rank Web Pages?
Google determines who ranks at the top of a SERP using a complex and ever-changing algorithm that takes hundreds of factors into account. Some of the most important factors include:
Relevance
The algorithm tries to determine how relevant a page is to the search query. This is done by looking at the keywords in the query, the searcher’s location, their device, the content of the page and the searcher’s previous search queries in a session.
Quality
The algorithm also tries to determine the quality of a page. This is done by looking at factors such as the expertise of the author, the accuracy of the information and the overall user experience.
- Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness (EEAT): Google also considers the EEAT factors when ranking pages. These factors measure how trustworthy and credible a website is.
- Google’s Helpful Content System: This system generates many of the signals used in the algorithm. It was most recently updated in May 2023.
- Google Documentation: Google provides extensive documentation on how to evaluate your content based on these guidelines. See Google’s fundamentals of creating helpful content. >>
-
Some of the content and quality self-assessment questions recommended by Google include:
- Does the content provide original information, reporting, research or analysis?
- Does the content provide a substantial, complete or comprehensive description of the topic?
- Does the content provide insightful analysis or interesting information that is beyond the obvious?
- If the content draws on other sources, does it avoid simply copying or rewriting those sources, and instead provide substantial additional value and originality?
Backlinks
Backlinks are links from other websites to yours. The more quality backlinks you have, the more authoritative Google will consider your website to be. A backlink is akin to a vote of confidence.
Technical Elements
Google evaluates technical elements such as:
-
Site speed: Google also considers the loading speed of your website when ranking it. Pages that load quickly are more likely to rank higher.
- Mobile-friendliness: Google now favors websites that are mobile-friendly. This means your website should be designed for easy viewing and use on mobile devices.
We discussed these elements in greater detail in our webinar about making the business case for SEO:
How to Build an SEO Business Case
The level of detail an SEO business case provides is more in line with an executive summary.
Your business case can include the following four parts.
1. SUMMARY
First provide an overview of SEO and how it works. Use all the valuable content in this article to concisely explain the basics. Then include your specific SEO proposal details.
2. OPPORTUNITY AND RISK
This section of your business case for SEO investment should list the benefits of SEO, such as increased website traffic, improved brand awareness and increased leads and sales. Get specific to the client!
- You can quantify estimates of organic traffic by:
- Showing the current positioning for keywords your client/prospect wants to be ranking for.
- Sharing estimates of keyword search volume and search traffic estimates, if you are in the top positions for those keywords.
- Align the SEO benefits with your business goals. Extrapolate forecasted volume to lead conversions and e-commerce sales, if applicable.
- You can underscore the risk of NOT investing in SEO by sharing competitor positioning in search results:
- Show where their competitors are ranking.
- Share search volume for your client’s/prospect’s branded searches vs. competitors’ branded searches.
- Research and share competitor organic search traffic.
3. COST ESTIMATE
Include a cost estimate for your proposed SEO efforts, including the time and resources required to implement SEO.
Of course, the cost of implementing SEO can vary depending on several factors, including:
- Size and complexity of the website.
- Keywords your client/prospect wants to target & the competitive landscape.
- SEO services recommended.
- Breakdown of in-house resources vs. outsourced costs.
4. ROI ESTIMATE
Finally, your business case for SEO investment should include an ROI estimate. Forecasting is possible at even the most basic level by using organic traffic estimates and then looking at existing goal conversion data and tracking by organic channel such as:
- E-commerce sales
-
Lead conversions:
(If not already set, recommend the client/prospect sets a monetary value for goal conversions):
- Request a Demo or Contact Us form submissions
- Email newsletter signups
- PDF downloads
- Engagement metrics
- Video plays
- Time on page
- Number of pages visited per session
We hope this article and template make it much easier for you to create your own business cases for SEO investment. Please let us know if you think something is missing. We’d love to hear from you!
If your company is interested in investing in SEO, please reach out to us at 3 Aspens Media!




